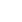
Aortic Stenosis
In Aortic Stenosis (AS), the aortic valve doesn’t open completely, restricting the blood flow from the left ventricle of the heart to the aorta and the rest of the body. The aortic valve is between the left ventricle and aorta (the largest artery in the body). The main function of the aortic valve is to open and close and allow blood to flow from the left ventricle of the heart to the aorta through which oxygen-rich blood is supplied to the rest of the body and the coronary arteries.
Symptoms of Aortic Stenosis
Symptoms of Aortic Stenosis vary from mild to severe and are normally developed during severe narrowing of the valve. Some people with Aortic Stenosis may not experience symptoms for several years.
Abnormal heart sound
Chest pain
Dizziness
Fatigue
Shortness of breath
Palpitations
Reduced hunger
Reduced body weight
If left untreated, Aortic Stenosis will weaken the heart and may cause heart failure. Thus, timely treatment will prevent fatality and improve quality of life.
Debunk Myths
Click each box to bust
each myth.
Myth
Heart diseases majorly affect men.
Fact
Heart disease is a cause of concern for both men and women.
Myth
Heart Disease is hereditary, hence one cannot do anything about it.
Fact
It can be prevented with healthy diet, blood pressure control and regular exercise
Myth
Heavy Drinking Affects the Liver not the Heart
Fact
Heavy alcohol consumption adversely affects both the liver and heart.
Myth
Heart diseases only affect the old, not the young.
Fact
Not true at all. Many young people have also succumbed to heart diseases.
Treatment of Severe Aortic Stenosis (AS)
Contemporary treatment options for AS include balloon valvuloplasty, Surgical Aortic Valve Replacement (SAVR), and Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI) / Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR)
This technique is a life-saving treatment modality for patients who are unwilling or at risk to undergo an open heart surgery. This novel, interventional technique is somewhat similar to angioplasty and is done in the Cardiac Catheterization Lab (Cath-lab)
An interventional procedure that requires placing a balloon catheter across the diseased aortic valve. It’s role is however limited and most patients will require a heart valve replacement therapy.
Surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) is the treatment of choice for many patients diagnosed with severe aortic stenosis, a tightening of the aortic valve in the heart. SAVR, where patient undergoes open heart surgery by cutting open the chest, can improve blood flow, reduce symptoms of heart valve disease and prolong life.
This is a less invasive procedure in which the diseased valve is replaced with a bioprosthetic valve using similar procedure as angioplasty.
In case the patient is asymptomatic or experiencing mild symptoms, the doctor may recommend regular monitoring of the patient’s condition through periodic follow-ups.
The doctor may advise some healthy lifestyle habits and prescribe medications to prevent complications or worsening of the present condition. It is important to note that medicines can be of help only if the disease is diagnosed in the initial stages without any major visible symptoms.
[Ref: ACC/AHA (American College of Cardiology / American Heart Association/ ESC (European Society Of Cardiology))]
Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation (TAVI)
Transcatheter aortic valve implantation (TAVI) or Transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) is the nonsurgical option. This technique is a life-saving treatment modality for patients who are unwilling or at risk to undergo an open heart surgery. This novel, interventional technique is somewhat similar to angioplasty and is done in the Cardiac Catheterization Lab (Cath-lab). Till date, valve replacement has been mostly done through open heart surgery wherein a new tissue/mechanical prosthetic valve is inserted in place of the diseased valve.
Open heart surgery is an invasive procedure and is known to have a longer recovery time and may be challenging for elderly patients (>65 yrs). Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR) technique is a life-saving treatment modality for patients who are unwilling or at risk to undergo an open heart surgery.